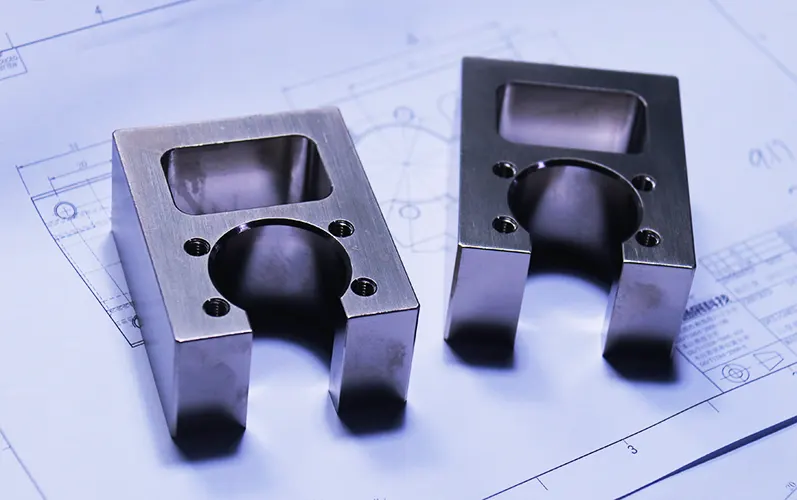
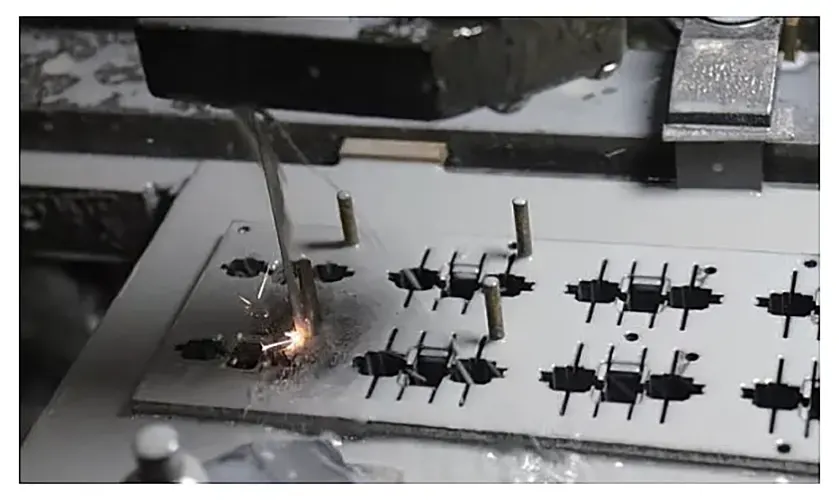
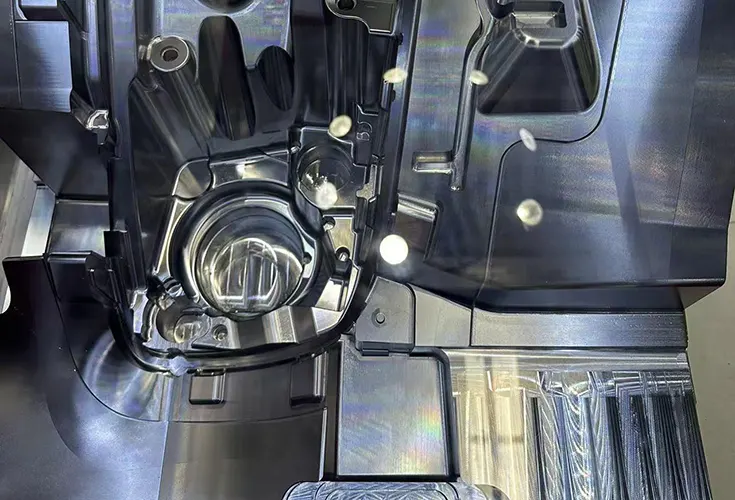
Precision Machining of Curved Surfaces Using a Photoelectric Edge Finder
With the rapid advancement of technology, an increasing number of industrial components featuring complex curved surfaces have emerged.
Precision Machining of Curved Surfaces Using a Photoelectric Edge Finder Read More »