Alodine services for you
With a focus on quality, our Alodine services provide parts that achieve high-quality surface directly, meet the demands of customers.

What is Alodine in Surface Treatment?
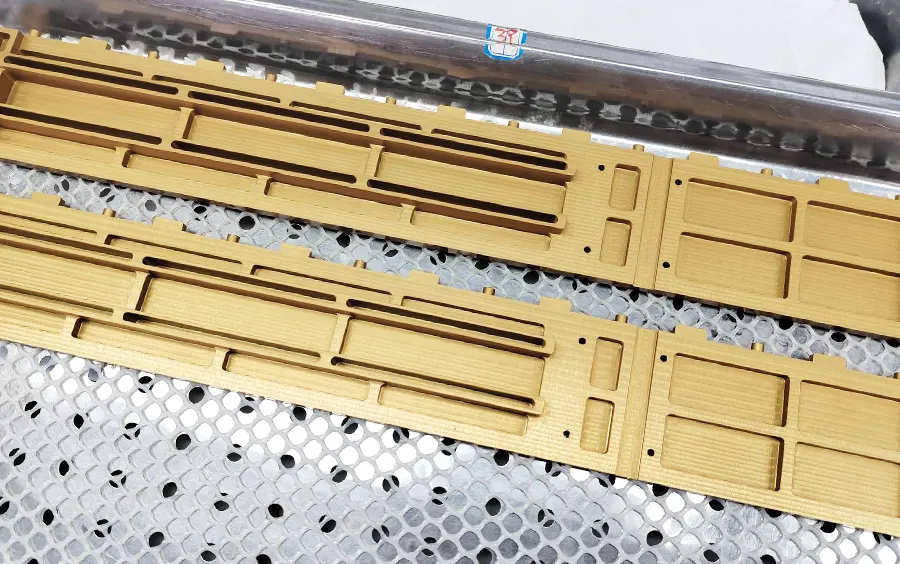
Alodine, also known as chem film or chemical conversion coating, is a surface treatment method used to enhance the corrosion resistance and paint adhesion of aluminum and other metals.
Alodine is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and military industries to improve the longevity and performance of parts and components exposed to harsh environments.
The coating not only provides corrosion resistance but also serves as a primer for paint or other surface finishes. Alodine can be applied using various methods such as dipping, spraying, or brushing, and the thickness of the coating can be controlled based on the specific requirements of the application.
We provide high-quality alodine surface treatment, offering exceptional protection for our customers’ products.
Main Feature
Provides corrosion protection, enhances paint adhesion, and maintains dimensional accuracy without altering part tolerances.
Advantages
- Corrosion Protection – Provides effective resistance against oxidation and corrosion on aluminum and its alloys.
- Electrical Conductivity – Unlike anodizing, Alodine leaves a conductive surface, making it suitable for grounding and bonding applications in aerospace and electronics.
- Paint/Coating Adhesion – Serves as an excellent base layer for paints, primers, or powder coating, improving adhesion and extending service life.
- Dimensional Stability – Coating thickness is extremely thin (typically <5 μm), so it does not alter tolerances, making it ideal for precision components.
- Cost-Effective – Compared to anodizing or plating, the process is relatively inexpensive and fast to apply.
- Repairability – Damaged coatings can often be touched up locally without stripping the entire part.
- Versatility – Compatible with a wide range of aluminum alloys and applicable to both large and small parts.
Disadvantages
- Environmental Concerns – Traditional Alodine uses hexavalent chromium, which is toxic and restricted under RoHS and REACH. This creates regulatory and disposal challenges.
- Lower Durability – While corrosion-resistant, Alodine coatings are not as robust as anodizing or hard coatings for wear resistance.
- Color Variability – Coating appearance can vary from iridescent gold to clear, making aesthetic consistency harder to control.
- Limited Thickness – Provides only a very thin protective layer; it cannot compensate for rough machining or damaged surfaces.
- Process Sensitivity – Requires careful surface preparation (cleaning, deoxidizing) to achieve uniform results. Poor preparation leads to weak protection.
- Performance Variability by Alloy – Some aluminum alloys respond better than others, requiring process adjustments.
- Replacement with Alternatives – In industries with strict environmental standards, Alodine may be replaced by trivalent chromium or non-chrome conversion coatings, reducing its use.

Design Considerations for Alodine Parts
Our CNC machines offer tight tolerances that meet industry norms, ensuring consistent precision and flawless piece fit.
Material Selection
Surface Geometry
Electrical Conductivity Requirements
Masking and Selective Coating
Thickness Control
Subsequent Coatings
Environmental & Regulatory Compliance
Inspection and Testing
FAQ about Alodine
For a clearer understanding of what we offer, here are FAQs on our Alodine process.
Frequently Asked Questions
All-in-One questions for Customer

What is the purpose of Alodine treatment?
The primary purposes of Alodine treatment are to provide corrosion protection, enhance paint and primer adhesion, and improve electrical conductivity in aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications. It is especially valuable for aluminum parts exposed to harsh environments.
What materials can undergo Alodine treatment?
Alodine is most commonly used on aluminum and aluminum alloys, though certain chromate conversion processes can also be applied to zinc, cadmium, copper, and magnesium. However, aluminum remains the most frequent substrate in industrial applications.
What are the advantages of Alodine treatment?
Key advantages include excellent corrosion resistance, enhanced coating adhesion, minimal dimensional impact (thin conversion layer), preservation of electrical conductivity, and suitability for selective masking. It is also cost-effective and widely recognized in aerospace and defense standards.
What are the disadvantages of Alodine treatment?
Disadvantages include the use of hexavalent chromium in traditional formulations, which is toxic and environmentally regulated. In addition, the coating provides less durability compared to anodizing, offers limited abrasion resistance, and requires careful waste disposal compliance.
What is the difference between Alodine treatment and anodizing?
Alodine treatment is a thin chemical conversion coating (typically <5 μm) that improves corrosion resistance and conductivity, whereas anodizing is an electrochemical process producing a much thicker oxide layer (5–25 μm or more) with superior wear and corrosion resistance but reduced electrical conductivity.
What industries commonly use Alodine treatment?
Alodine is widely used in the aerospace, defense, automotive, marine, and electronics industries. It is particularly valued for aircraft components, electrical housings, connectors, and aluminum structures that require both corrosion protection and paint adhesion.
What color is Alodine coating, and does it affect performance?
Alodine coatings typically appear in gold, iridescent yellow, or clear finishes depending on the formulation and application. The color itself does not impact performance but serves as a visual indicator of coating presence and uniformity.
What standards govern Alodine and chromate conversion coatings?
Common standards include MIL-DTL-5541 (U.S. military specification) and ISO 8081. Compliance with these standards ensures that Alodine-treated parts meet strict aerospace and defense requirements for corrosion resistance, adhesion, and conductivity.
Are there environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional Alodine?
Yes. Due to environmental and health concerns with hexavalent chromium, trivalent chromium-based and non-chrome conversion coatings have been developed. These alternatives reduce toxicity while still providing corrosion resistance and paint adhesion, although they may not always match the performance of traditional Alodine in extreme conditions.








