Polishing services for you
With a focus on quality, our Polishing services provide parts that achieve high-quality surface directly, meet the demands of customers.

What is Polishing in Surface Treatment?
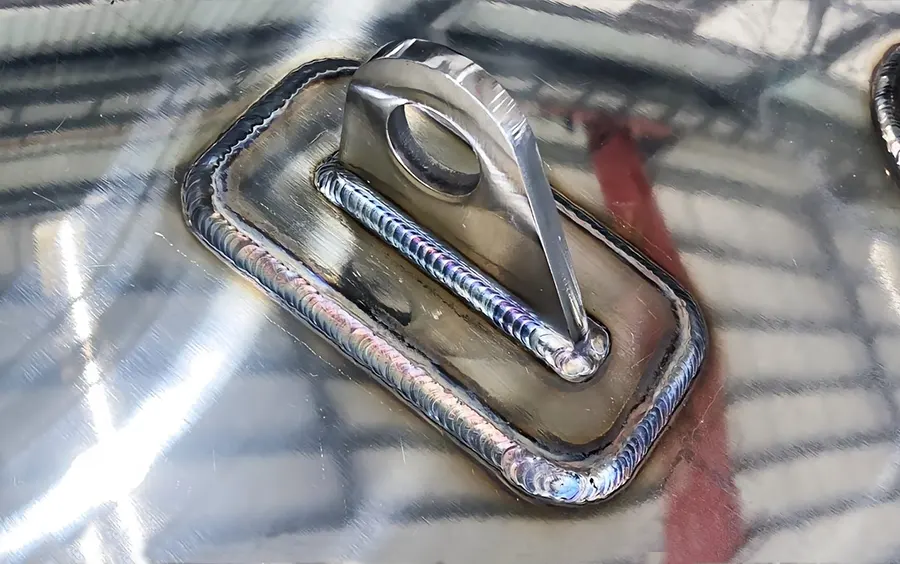


Polishing in surface treatment is a crucial process that involves the removal of imperfections on a material’s surface to achieve a smooth and shiny finish.
This technique is commonly used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics to enhance the aesthetic appeal, improve functionality, and prolong the lifespan of components.
Polishing is typically performed using abrasive materials, such as sandpaper, abrasive discs, or polishing compounds, in conjunction with polishing machines or tools.
The process begins by gradually refining the surface of the material through successive stages of abrasion, starting with coarse abrasives to remove larger imperfections and progressing to finer abrasives for a smoother finish.
Polishing not only improves the appearance of the material by eliminating scratches, burrs, and other surface defects but also helps in enhancing corrosion resistance and facilitating easier cleaning and maintenance.
Main Feature
Creates a smooth, reflective surface by removing scratches, imperfections, and oxidation, resulting in improved aesthetics, reduced surface roughness, easier cleaning, and in many cases, enhanced corrosion resistance.
Advantages
- Produces a smooth, shiny, and visually appealing surface.
- Removes scratches, tool marks, and oxidation for improved quality.
- Enhances corrosion resistance by eliminating crevices where contaminants can settle.
- Reduces friction and wear in moving or contact surfaces.
- Facilitates easier cleaning and maintenance.
- Can prepare parts for additional coatings or surface treatments.
Disadvantages
- Removes a thin layer of material, which may affect tight tolerances.
- Labor-intensive and time-consuming for complex geometries.
- Increases production costs, especially for mirror-like finishes.
- May not be suitable for parts with sharp corners, deep holes, or intricate features.
- Highly polished surfaces may highlight fingerprints, smudges, or minor defects.
- Offers no added protective coating by itself—surface can tarnish or dull over time without maintenance.

Design Considerations for Polishing Parts
Our polish treatment provides a sparkling surface that satisfy industry requirements, ensuring consistent accuracy and seamless piece alignment.
Material selection
Surface condition
Part geometry
Tolerance and dimensional accuracy
Surface finish requirements
Accessibility
Application environment
Cost and time
FAQ about Polishing
We’ve gathered the most relevant questions and answers to guide you through our Polishing Services.
Frequently Asked Questions
All-in-One questions for Customer
Which materials can be polished effectively?
Commonly polished materials include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, titanium, and certain plastics. The ease and results of polishing depend on material hardness and surface properties.
How does polishing differ from buffing?
Polishing focuses on smoothing surfaces by removing fine scratches and irregularities, while buffing enhances gloss and shine after polishing. Both processes are often combined for optimal results.
Does polishing affect part dimensions?
Yes, polishing removes a small amount of material from the surface. Designers must account for this when tight tolerances are required, especially for precision components.
What industries commonly use polishing services?
Polishing is widely used in medical devices, aerospace, automotive, jewelry, optics, and food processing industries, where both functional and aesthetic finishes are critical.
Can polishing improve corrosion resistance?
Yes. By creating a smooth, scratch-free surface, polishing reduces crevices where moisture and contaminants can accumulate, thereby improving corrosion resistance when combined with protective coatings.
What types of finishes can polishing achieve?
Polishing can deliver finishes ranging from satin and brushed effects to high-gloss mirror finishes, depending on customer specifications and application needs.
Is polishing suitable for complex part geometries?
It depends on accessibility. Flat and curved surfaces polish easily, while sharp corners, deep recesses, or blind holes may require specialized tools or alternative finishing methods.
How does polishing compare to other surface treatments?
Unlike coatings or platings, polishing does not add material but instead refines the existing surface. It is often used in combination with treatments like anodizing, plating, or passivation to achieve both aesthetic and functional performance.