A set of high-quality injection molds is inseparable from reasonable design and exquisite processing. Traditional mold design mainly relies on the experience of designers. After the mold is designed and processed, it often needs to be repeatedly debugged and modified before it can be officially put into production. The efficiency is too low, can no longer be used, and can even meet production needs. Even experienced engineers can take weeks or even months to design a new mold, and accuracy is difficult to guarantee.
With the continuous improvement of professional software, the utilization of injection mold flow analysis technology can analyze the rationality of mold design in advance, reduce the number of mold trials, accelerate product development, and consequently enhance enterprise efficiency. While the use of high-end CAD/CAE/CAM design software for manufacturing can significantly boost mold design efficiency and shorten manufacturing time, it solely approaches issues from a design perspective and may not adequately address certain challenges in actual injection molding production.
Moldflow is professional software utilized for designing and manufacturing plastic products and molds. It can simulate the entire injection molding process and its impact on injection-molded products, evaluate and optimize the entire process, and analyze plastics prior to mold manufacturing. This optimization spans product design, production, and quality, offering a comprehensive solution for enhancing enterprise product design and manufacturing. It assists technicians in optimizing various key points throughout the entire process.
So how does it work? Let’s take a practical example to illustrate how it can provide designers with efficient negotiated solutions.
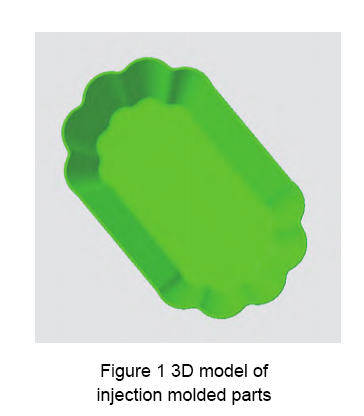
As depicted in Figure 1, the injection molded part is a small plate. If the mold design is flawed, the material selection is inappropriate, or the process parameters during injection molding are not properly set, the resulting injection molded parts may exhibit quality defects such as warping deformation, flash, weld marks, and prolonged molding cycles.
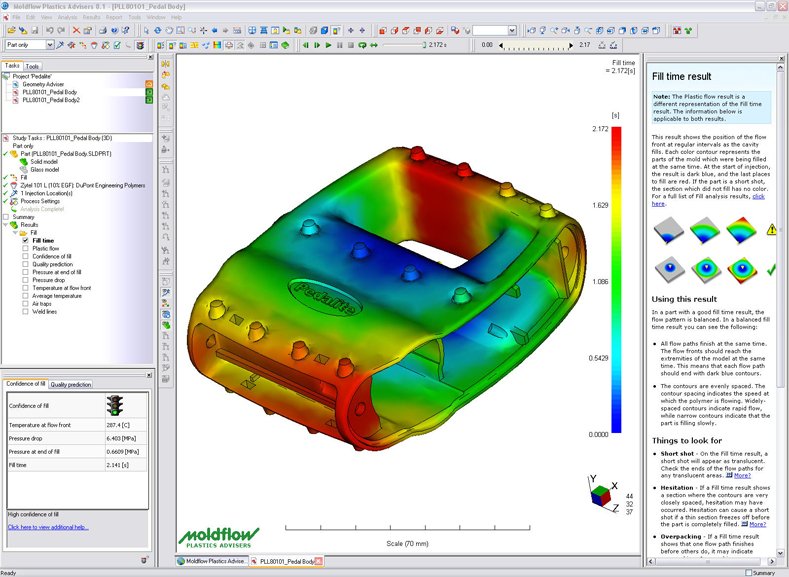
To enhance mold development efficiency, reduce the development cycle, minimize the number of mold trials, and improve the product qualification rate, Moldflow software is employed to conduct mold flow analysis on the injection molding process of these parts prior to mold development. Initially, the optimal gate position is determined and filled with injection molded parts.
Subsequently, molding analysis calculations including filling analysis, holding pressure analysis, and warpage analysis are utilized to predict potential quality issues of the injection molded parts.
Finally, by analyzing optimization plans, the best materials for injection molded parts are selected to enhance product quality, production efficiency, and the qualification rate of injection molded parts while concurrently improving efficiency, shortening the product development cycle, and reducing mold development costs.
Mold flow analysis of injection molded parts
1. Model modeling and pre-processing
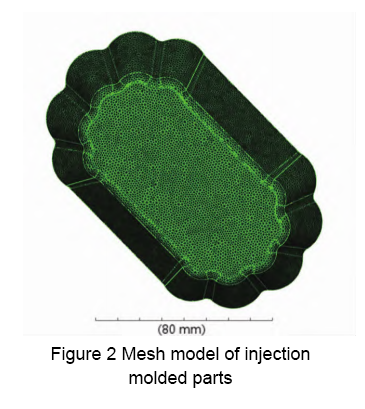
The three-dimensional model of the injection molded part is shown in Figure 1. The overall dimensions are 140 mm × 85 mm × 3 mm, and the wall thickness is 1.5 mm. A 3D solid mesh model is used to divide the finite element mesh, and the global mesh side length is 1.3 mm. A CAD mesh model of the small plate was created, with a total of 822,409 mesh units. The mesh model was diagnosed and repaired, with an average aspect ratio of 7.38, as shown in Figure 2.
2. Analysis of optimal gate location
The positioning of the gate directly impacts the flow of the melt within the mold cavity, consequently influencing the orientation of polymer molecules and post-molding product warpage. Thus, selecting a suitable gate position is paramount in mold product design.
In the mold design stage, Moldflow’s powerful analysis capabilities can be utilized to comprehensively assess flow resistance and balance, determining the optimal gate position to ensure flow equilibrium. This enables rational mold system and gate position design, mitigating potential issues and enhancing the success rate of initial mold trials. Consequently, it shortens the product design and launch cycle, significantly reduces production costs, and bolsters corporate competitiveness.